What is the future of RPA?

Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, differs from other classical automation solutions in that its ultimate goal is to replicate human behavior when interacting with computer interfaces. This form of digitalisation allows organisations to automate functions with a much greater reduction in time, workload and costs, eliminating errors while increasing the efficiency, performance and precision of processes, as it focuses mainly on the automation of highly repetitive routine tasks.
Ongoing research developments show that RPA robots are already capable of imitating many human actions and this process spectrum may increase even further in the future.
Robots are already capable of automatically logging into apps, moving files and folders, copying and pasting files, filling in data or forms, extracting structured information from documents, etc. The application universe of RPA is therefore gigantic and can play a crucial role in freeing human employees from a multitude of tedious or repetitive tasks, allowing them to process them much more quickly.
Present situation
According to data, global spending on automation systems and artificial intelligence applied to business processes is expected to grow strongly through 2023, maintaining the growth rate experienced over the past few years, and the global market size is expected to grow to $10.4 billion by 2023 as well.
These estimates, published in January 2020, suggest that by the end of this year, $9.6 billion will have been invested in intelligent process automation. That is, in all those computer tools designed for autonomous decision making, simulating human behavior and associated business processes. This includes automatic self-learning systems, data mining, pattern recognition tools and natural language processing. Specifically, 4 billion will be allocated to RPA, growing by more than 50% in just three years.
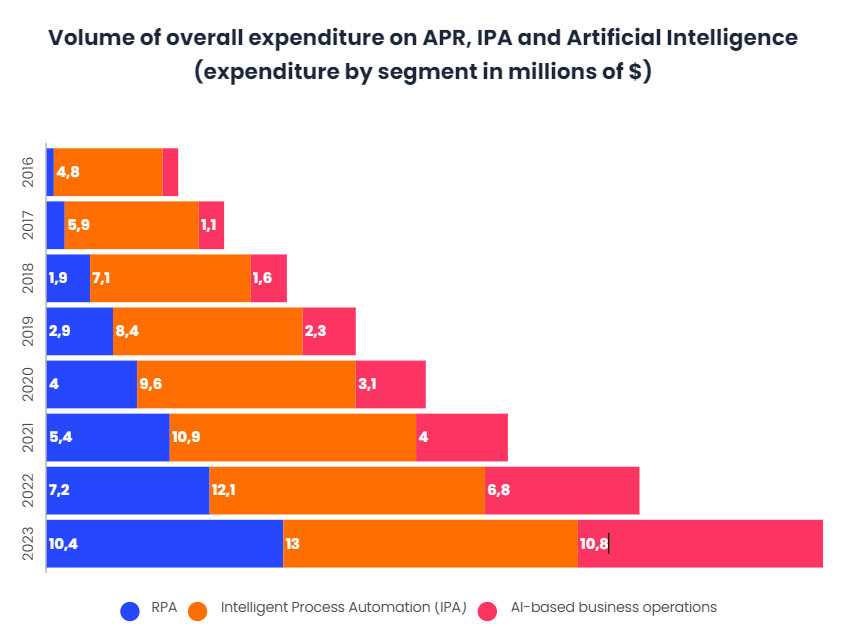
However, these estimates issued in January were probably still not taking into account the real impact that the Covid-19 crisis was going to cause in the following months. This is where the question now arises as to whether this impact can lead to a much stronger and faster take-off of PPP due to its potential to reduce costs and speed up professional tasks at a time when it seems to be becoming more necessary.
RPA in a post-covid world
The COVID-19 crisis has pushed companies to innovate like never before, and as life is slowly returning to normal and the health crisis is lessening, companies around the world are starting to think about how to change and evolve their businesses, as the economic effects of this crisis will continue to be present.
Many companies in various industries are facing a number of challenges as a result of the COVID-19 crisis:
- Reduction in staff or equipment due to teleworking.
- Protecting the health of workers with distance.
- Decrease in demand for some products and services.
- Large increases in demand for some products and services.
- Need to improve processes to increase productivity and reduce costs.
Many experts agree that this new crisis has created a very lasting and fundamental change in the way companies work, and recognize that there is little chance that many companies will be able to return to the way they were before COVID-19 in a short or medium term. However, these companies have to accept the changes they have to make in their businesses, due to the situation, in order to stay in the market, be more resilient in the future and be competitive, something that is achieved through automation, and in particular the deployment of RPA solutions, which will be key for those organisations that are visionary and accept change.
Companies and organisations that had not used this technology before the crisis are now seeing the benefits of scalability, flexibility and diversity of these RPA applications, and many of these companies are starting to use them.
So far, we have already begun to see this trend being successfully applied to health and pandemic containment work.
RPA in health
The most imminent field of work where APR can act as a response to the impact of Covid-19 is that of automating hospital processes to prevent system collapse, or help reduce system saturation.
ARP software is being used by healthcare organizations to help them accelerate and improve the management of critical processes, freeing doctors and employees from certain tasks so that they can focus on a rapid response to the most serious problems.
These systems are being used, in medical processes, to automate tasks such as:
- Manage the huge volume of test requests in hospitals: automating the check-in processes in hospitals, eliminating human error, avoiding manual data entry into the computer system, the use of paper and, in general, streamlining the service.
- Reducing test waiting time: performing a medical test can, in some cases, take up to six hours. Robotizing the processes of care and management of the request for a test can significantly reduce these times, unblocking the bottlenecks and saturation of waiting rooms.
- Faster order processing: To solve the exponential increase in demand for certain medical products, order processes can be automated through RPA and the request can be sent to manufacturers much faster, relieving employees of that management time.
- Support in call center management: another area of work that has seen an increase in demand is that of call center queries. Customer service agents can rely on RPA systems to access a patient/client’s data faster, resolve calls with general and routine queries and reduce waiting times on the phone.
- Prepare the remote workforce: automating tasks such as registering new equipment for remote workers, setting up VPN access networks, etc.
For example, at the Mater Hospital in Dublin, Ireland, RPA technology is being used to process Covid-19 tests much more quickly. The hospital not only gets the patient’s results almost in real time but also significantly reduces the associated administrative processes
Each nurse can save up to three hours of work per day in the administrative management of these test processes which previously included tasks such as filling out forms. By digitizing and automating the entire process, it also becomes more efficient as each patient’s data is recorded and is easier to access again at a later date.
RPA in the insurance and financial sector
The opportunities that RPA can already provide to the insurance and financial sector are very varied. For example, there are insurance companies that have experienced an exponential increase in the volume of work due to the growing demand for benefits. This especially affects the entire insurance staff who are already working remotely or virtually from home. Some of these insurance companies have implemented robots capable of supporting the massive management of processes and transactions, freeing employees from a great deal of administrative work and allowing teams to provide agile service to customers working from home.
As for the banks, they have been forced to move a large part of their workforce to their homes and have promoted the use of digital banking and remote assistance systems among their customers.
A very clear example of an area of banking work where APR could be of great help is that of call and customer service centres. Where RPA systems may be able to resolve basic management issues that previously required human support. They can also support home-based agents to quickly and easily access customer financial information, thus significantly reducing waiting times.
Another huge field of application is that of regulatory compliance processes, where RPA can help:
- Process workflows more easily and quickly
- Control costs: using RPA instead of manual processes allows you to increase productivity, reducing backlogs and bottlenecks, etc.
- Improve the risk profile: Reduce the risk of error to almost zero, decreasing the probability of error compared to manual systems. Allows teams to be freed up to focus more of their time on important research and analysis tasks. It also makes it easier to update systems as quickly as regulatory requirements change.
An example of a financial institution where they are applying RPA in this area is the bank of India Federal Bank. There, they are using RPA to streamline regulatory compliance operations, reducing costs and increasing the scope of regulatory requirements in half the time.
Conclusions
Organizations around the world, and in all types of industries, are increasing their adoption of process automation systems to speed up and improve their response to changing work environments.
From lightening the administrative workload, to enabling new remote working possibilities, to unblocking waiting times in customer service centres, the opportunities offered by RPA for the new demands on financial institutions are very varied.
The crisis generated by the pandemic can serve as a great global experiment to understand to what extent process robotics can completely change current workflows by being able to replicate almost any human action.
In the future, most of the interactions that human employees currently carry out with their machines may become subject to robotization.


