The revival of UWB technology

There is an old but rather unknown technology that has been gaining strength in the last two years and is starting to become popular, namely UWB or ultra-wideband technology. It was at the end of 2019 that the UWB concept resurfaced with the introduction of the iPhone 11 Pro, which became the first smartphone to incorporate a chip with this technology.
At that time, experts started talking again about this forgotten technology, and it is now considered to play a very important role in the field of smart homes, Virtual and Augmented Reality, security and geolocation. In fact, it is estimated that UWB’s global market will grow from $1.1 billion in 2020 to $2.7 billion by 2025, at a compound annual rate of 19.6%.
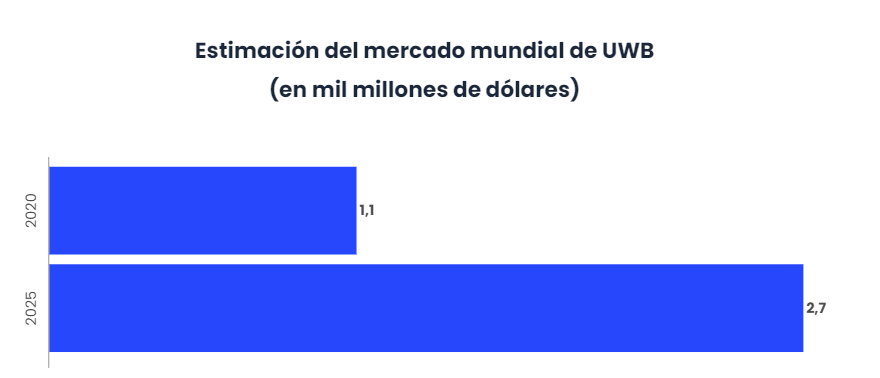
The main factors that are driving this growth are the deployment of this technology on various mobile devices, the growth in demand for real-time location systems and the growth in the adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
UWB: the great innovation in wireless technology
UWB is a protocol that allows short range wireless communications that, like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, uses radio waves to allow devices to communicate with each other. But it differs substantially in that it operates at a very high frequency. As its name suggests, it also uses a wide spectrum of several GHz.
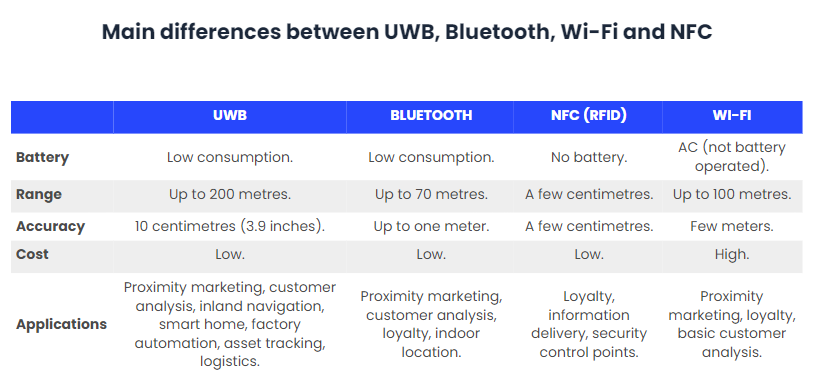
UWB transmits data over short distances and accurately determines location by measuring how long it takes a radio pulse to travel between the devices. In addition, due to the wide spectrum, data can be sent very quickly without losing accuracy. UWB can achieve data rates from 4 Mbps to 675 Mbps or higher, depending on the frequency. That’s much faster than standard NFC speeds of 424 Kbps and Bluetooth speeds of 2.1 Mbps, but not as fast as the 2 Gbps speeds that can be achieved with WiFi-6.
A UWB transmitter sends billions of radio pulses across the wide-spectrum frequency and a UWB receiver then translates those pulses into data. In addition, UWB achieves real-time accuracy because it sends up to one billion pulses per second (approximately 1 per nanosecond).
In the early 2000s, UWB technology saw limited use in military radar and covert communications, and was briefly used as a form of medical imaging, such as remote cardiac monitoring systems. At that time, the cost of implementation and lower than initially expected performance limited the use of UWB in consumer products.
Today, UWB chips are cheap and small enough to be placed in other devices, and the industry claims that it could be more successful than Bluetooth because it has a higher speed, is cheaper, uses less energy, is safer, and provides superior location and device range information.
Benefits and disadvantages of UWB technology
UWB technology enables superior performance compared to traditional broadband systems. In addition to this, its benefits include:
- Low power consumption: UWB is a low power system, which is a key factor for mobile devices in terms of battery life and practical usability.
- High accuracy: Instead of relying on signal strength, UWB uses ToF (Time of Flight), TWR (Two-Way Range), TDoA (Time of Arrival Difference), AoA (Angle of Arrival) techniques, etc. to determine the distance to another device. In addition, with multiple antennas, UWB can also measure the angle from which the signal arrives.
- No signal interference: UWB uses a frequency of 3.1 to 10.6 GHz, so there is a very limited probability of any signal interference, unlike with Bluetooth and Wifi.
- Ultra-fast: Bluetooth takes at least two seconds to detect location, UWB is a thousand times faster, which means there are no delays and the user experience is virtually perfect.
However, there are also certain disadvantages of this technology. One of these is the loss of transmission power which limits the UWB signals so that they can only communicate over a short range. But the biggest disadvantage is that other technologies such as Wi-fi or Bluetooth can interact with virtually all devices that currently exist, UWB has only just begun and can only be used on a few devices. However, UWB is expected to catch up with these two technologies quickly, as many smartphone manufacturers are doing the same as Apple did in its day and are including UWB technology in their devices.
What are its possible uses?
With its high accuracy, fast transmission and high reliability, UWB technology is ready to help companies locate moving people and objects in all kinds of environments and processes.
UWB has an advantage in both accuracy and security over Bluetooth and WiFi technologies, and that advantage can be used in many different use cases.
- Smart Car: With UWB technology you can achieve greater safety and comfort. It can be used to unlock a car with a smartphone as soon as the user approaches it. The car’s internal chips communicate with each other and calculate the owner’s position by locking the car in the event that someone other than the owner tries to open it. At the same time, thanks to the precision of the location and the determination of distances around the vehicle, the car can detect whether there are people or animals nearby, has automated parking functions, and easy access to parking spaces or automatic payment on exit are some of the possible applications in this field.
- Contactless payments: It is safer than NFC technology and the user can leave his smartphone in his pocket without having to take it out to pay.
- Secure access to a building: With UWB the doors to a secure area within a building can be automatically opened as soon as the user approaches them.
- Retail: UWB can provide useful information about a product that a person has just picked up, as well as a special offer to buy one. Chips can be placed in shopping trolleys to keep track of them, or to know where and how long customers stay in the shop. Location and data analysis through UWB provides the answers and opens up new forms of marketing.
- Tracking sports and fitness: In team and extreme sports, the demand for performance and movement data is particularly high. With UWB technology, players on a pitch can be tracked to reproduce their movements in real time, as well as seeing both individual and team statistics and tactical analysis all in real time. The location of a football can be updated 2000 times per second.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: With UWB technology a user can see from his smartphone and in Augmented Reality the exact location of other objects also equipped with UWB. In addition, this technology is a Mixed Reality facilitator, as it helps devices to close the gap between the physical and digital worlds, for example, a user can see a map of a shop, from his smartphone, and navigate through it to find the products he needs.
- Health Wearables: UWB technology within a wearable device such as a wristband can monitor body temperature, oxygen saturation levels, body movement and heart rate 24 hours a day.
- Medical Radars: UWB can be used to monitor a person’s breathing and heartbeat remotely by reading the reflected UWB signals.
- Indoor positioning: With UWB a person can position themselves precisely within a site, know where they are and where they want to go. For example, at an airport to find the boarding gate or in a shopping centre to find a particular shop.
- Smart Home: The uses of UWB for smart home are many, from locating lost keys to unlocking and automatically locking doors when approaching or leaving, and smart access restrictions for pets. Lights, speakers and any other connected devices with UWB detection capability will be able to follow users from one room to another, for example adjusting the volume of a speaker depending on where it is located or changing the Netflix profile depending on who turns on the TV.
- UWB for warehouses: With UWB you can actively track the people working in the warehouse, the machines and equipment inside, or find a product on a shelf.
UWB and its use against Covid-19
With the arrival of the Covid-19, the need arose to implement a series of strategies to combat it. Two of the most important strategies for dealing with the pandemic have been social distancing and contact tracking or tracing. Since then, many organisations worldwide have used UWB technology to address the Covid-19 crisis, as the accurate real-time measurement of location and distance enables UWB technology to determine the exact location of a device to within inches, both indoors and outdoors.
This accuracy makes UWB extremely well suited to the much-needed contact tracking and social distancing applications being developed in many countries to help prevent the spread of the pandemic. In fact, UWB is the only technology available that can offer the level of accuracy required for this type of application.
Unlike other wireless technologies, UWB provides the accuracy needed to be absolutely sure whether someone was close enough to others to transmit the virus, as it can calculate the distance between people who are inches apart with precision.
UWB is also used in social distancing applications, which are designed to ensure that people maintain a safe distance from each other. For example, in one company an employee can wear a UWB wearable and it can alert him, in real time, when he gets too close to someone. This solution can reduce the spread of the virus in a company, as well as improve the security of employees.
Conclusions
Although this is a technology that started quite a few years ago, it is as if it were new, as it is now that companies are starting to work on it and incorporate it into their devices, but this is only the beginning of a possible revolution in UWB technology.
Its potential is just beginning to be seen. The technology is enabling a wave of applications that use high-precision distance and location detection to provide new experiences and capabilities, including many applications that were previously not possible.
UWB can potentially be used in almost everything from wireless printers to contactless payments, and from the automotive sector to healthcare, smart home, logistics, retail or sports. It all depends on finding that one application or function that makes it worthwhile.
It is important to note that UWB technology does not necessarily have to replace Wi-fi, NFC or Bluetooth, as it can work with them.
The potential of UWB is enormous and although it will probably take a long time to see this technology more widely used globally, one thing is certain: UWB is poised to change the way people live and work.


