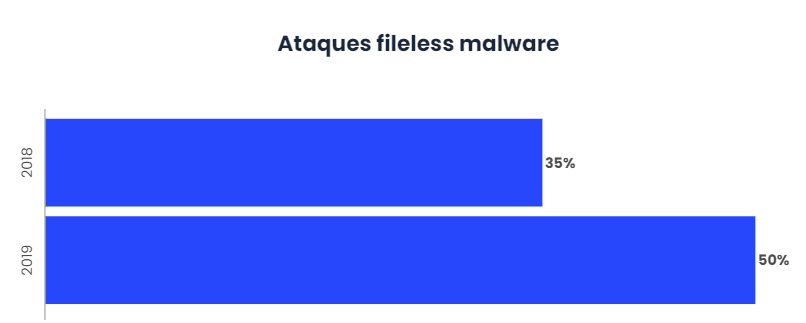
In 2019 the 50% thy bets will be fileless malware

The cybersecurity landscape is changing, different types of cyberattacks are evolving and gaining in popularity as defenses improve. Currently fileless malware is one of the most popular attacks among cybercriminals.
These attacks are growing in sophistication and frequency, and are proving to be particularly successful against most organizations because a large percentage of previous security solutions were designed to detect malware based on files residing on disk, not memory.
This situation has led to approximately 35% of all attacks suffered during 2018, and it is estimated that by 2019 they could reach 50% of the total malware attacks.
Due to their difficulty in detection and subsequent blocking and removal they are almost ten times more likely to succeed than file-based attacks. Part of this success is because, what began as a banking Trojan has expanded its operations and now frequently targets companies in an attempt to collect access credentials and data as it can, potentially exploiting them in an effort to obtain intellectual property and trade secrets.
Emotet, so far the most dangerous
The research shows that the new malware fileless being developed and deployed features and techniques that allow cybercriminals to go further than before in terms of infection, detection evasion and persistence .
Some of the most dangerous attacks are Emotet, TrickBot and Sorebrect, among others, which allow attackers to perform activities that are not detected by traditional security systems.
The rise of Emotet Trojans aimed at banking companies is mainly due to the virus that contains a spam module that allows attackers to mass send malicious payloads to email addresses found in the system Selected.
Detection of Trojans targeting banks increased by 84% in the last quarter of 2018, while attacks targeting customers increased by only 27%.
With the US at the forefront, the UK has been the European country where the most Emotet infections have been seen during 2018.
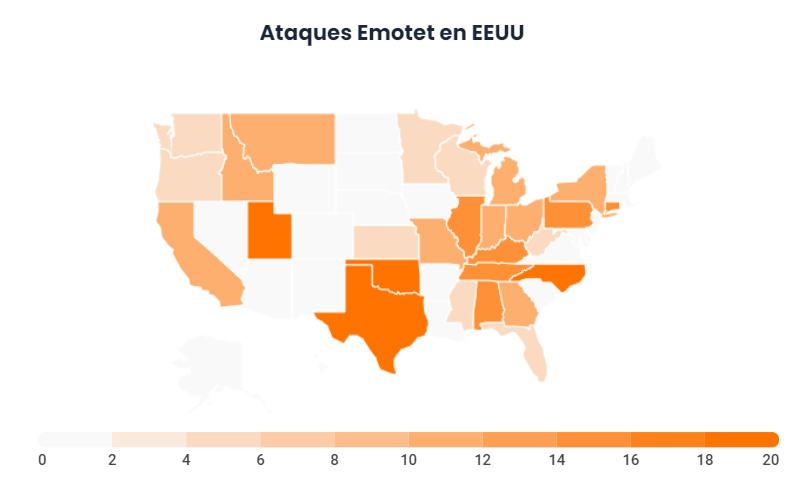
However, since the beginning of 2019, Latin America has suffered an increase in these attacks through Spanish-endeab-e-mails that invoke CMD and POWERSHELL commands. For example, the Chilean bank Consorcio, was at the end of 2018 one of the last victims of this cyberattack. The Trojan would have sneaked into the network via a common phishing attack.
How to protect yourself?
Because the threat posed by fileless malware is so different from that posed by other malware, organizations need to create a specific mitigation plan with many components.
Risk mitigation plans, including fail-safe operations, ensure that if a failure of the equipment, process or system occurs, it does not spread beyond the immediate surroundings of the failing entity.
In the face of a malware filelessattack, the mitigation plan must be proactive enough to monitor operations performed by window management services [WMI] and PowerShell to identify any unwanted tasks.
It is also a good idea to disable the command-line shell script language, including PowerShell and Window Management instruments, where it is not required. However, this action can have a significant impact on productivity because PowerShell has become increasingly important to IT departments in automating critical processes.
Therefore, a mitigation plan should include UPS systems for workstations, so that devices cannot be shut down in the event of a power failure from infection identification to investigations.
And what about “more traditional threats”?
So far there has been talk of malware fileless attacks, due to their imminent boom. However, more traditional threats will not disappear in the near future.
During 2018, large-scale data breaches, consumer privacy issues, and hardware-level vulnerabilities were addressed by the holders. In the Asian region, for example, Singapore’s massive data leak in the healthcare sector and cryptocurrency-trading hackers in Japan and Korea were some of the biggest calls for attention about inadequate data protection Confidential.
Currently, the average cost of a data breach is $7.5 million, however, this figure is expected to increase in value year on year. While all organizations are potential targets of cyberattacks, industries that have high monetary value data are the most important objectives, which include financial services, the area of health, the area government, automotive and retail sector.
Although cybersecurity is always touted as a priority, SingHealth’s leak of 1.5 million patient records showed that even sensitive sectors such as the health area may lack adequate protection against attacks Cyber.
Because of the impact on human lives, an attack on smart health systems could have significantly greater consequences than a data breach, making the issue of cyberattacks very relevant to organizations.
By 2019, cyberattacks will not disappear, however, they will adapt to new situations by modifying their form of attack.
Conclusions
Within the high number of cyberattacks, those that are performed without a file, are gaining great boom because most of the security solutions past and present are designed to detect file-based malware. This growing gap in protection has led to a tremendous increase in malware fileless attacks.
That is why it is important for companies to define a robust mitigation plan, which allows to monitor all the actions that are happening on the devices. This plan must be accompanied by a number of preventive actions such as two-step authentication or password enhancement.
While still taking into account attacks fileless malware, it is important that organizations think about their cybersecurity plan for this 2019, and do not leave out the more traditional threats, carried out through phishing campaigns, fake videos or massive attacks aimed at IoT devices as these will also continue to grow.


