Computing Where It Matters: Edge Computing Gaining Ground on Cloud

Cloud computing (CC) refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, databases, storage, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. Edge computing (EC) differs from CC in that it's used to process time-sensitive data (low latency) while CC is used to process data that is not time-driven. Besides latency, EC is preferred over CC in remote locations, where there is limited or no access to a centralized cloud server.
Many enterprises deploy their AI applications using EC to process data at the very location of its generation. Instead of cloud processing doing the work in a distant, centralized data reserve, EC handles and stores data locally in an edge device. This is the reason EC has also gained significant momentum over the years.
Market opportunity: Cloud computing and edge computing in the US
Since EC is a relatively new concept, the CC market is significantly larger owing to the substantial awareness and adoption over the years across industries. In fact, no industry has yet to adopt CC in some capacity. This is because any business that uses the internet is also using CC in one way or another. At the same time, EC also presents opportunities as its growth is expected to be almost double the growth of CC in the coming years. Refer to the could computing and edge computing data below, drawn from Grand View Research.
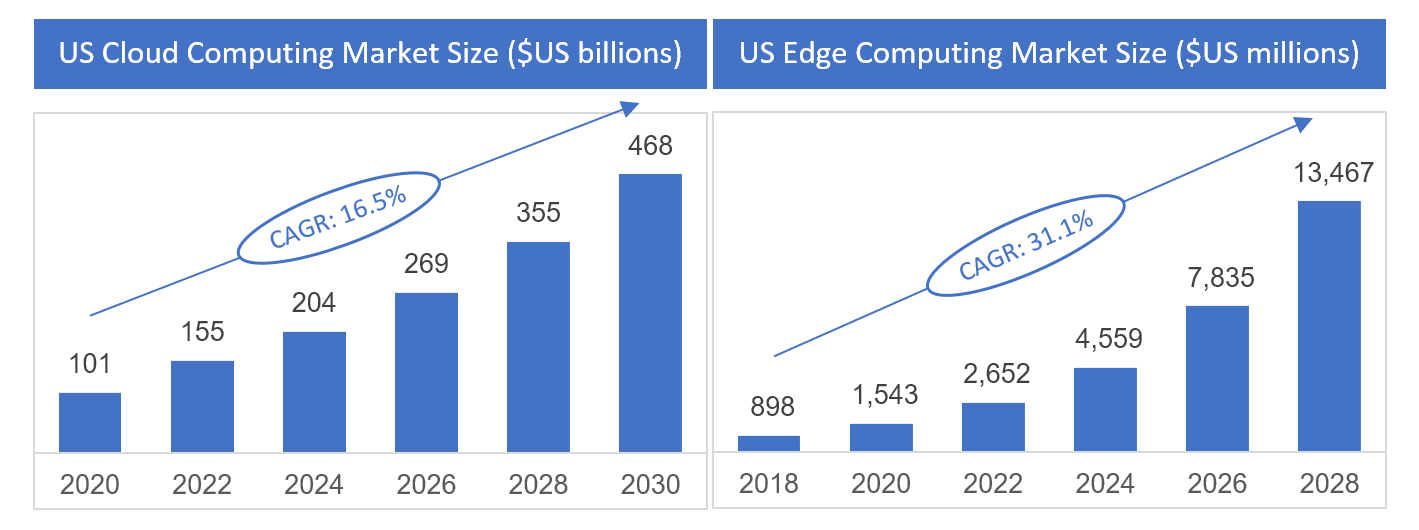
Popular subsegments in CC: Software as a service (SaaS) is the most dominant subsegment representing over half of the market, followed by infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS).
Popular subsegments in EC: Since hardware is a key element of EC, it's expected to represent the major share of the market, followed by the platforms that will be leveraged to manage the installed hardware.
Key use cases for 'computing at the edge'
Here are some industry examples of why edge computing is positioned for incredible growth:
- Retail: IDC FutureScape: Worldwide Retail 2022 Predictions reveal that “by 2025, 90% of the top 2000 retailers will employ EC to harness the explosion of data in stores for better workforce productivity and customer experience while reducing costs by 20%.”
- NVIDIA launched its EC stack EGX in 2019. Walmart uses EGX to analyze 1.6 terabytes of data/second
- Customer Experience (CX): Since customer interactions across sectors are becoming digital-first, the performance of websites and apps plays a major role in CX. A 2020 study by Deloitte Digital revealed that a 100-millisecond improvement in mobile retail website speed results in an 8.4% growth in customer conversion. EC can and will deliver that time reduction.
- Autonomous vehicles: Autonomous technology is the future of both passenger and commercial vehicles. Such vehicles are equipped with several sensors, and their data needs to be processed in real-time. This processing can be delivered through EC, through a concept called IoT edge, to reduce accidents, improve safety, enhance efficiency, and decrease traffic congestion.
- As an example, devops.com notes that Tesla has created a processor with six billion transistors. As compared with NVIDIA GPU, it boosts performance by 21x and has been installed in Tesla Model S, Model 3, and Model X models.
- Oil and Gas (O&G): Real-time monitoring of assets and operations is of the utmost importance for O&G companies, Deloitte leaders say. O&G plants are often located in remote locations and EC enables data processing close to the facility. Additionally, linking EC with the cloud allows the remote team to monitor a large number of sites.
- In December 2020, Hivecell, an EC services provider, announced that WPX Energy has implemented its ‘Edge-as-a-Service’ solution. It has been adopted for real-time decision-making and control optimization at the drilling and completion operations in the oil fields of West Texas and North Dakota.
- Healthcare: Currently, healthcare teams are using EC devices for automated delivery of care, remote patient monitoring, improved speed and accuracy of diagnoses, and many other use cases.
- For instance, a Hewlett Packard article notes that UCLA Health and Massachusetts General Hospital have deployed edge devices like Hyperfine's portable MRI machine to capture brain scans at the patient's bedside in real time.
- Space: The application of EC isn't just limited to global business operations, but to speeding up space exploration as well. For instance, NASA has started leveraging EC for data processing up in space, rather than sending it back to Earth.
- Specifically, IBM covers how the International Space Station (ISS) astronauts are currently studying microbial DNA through ‘edge’ technology. Using the traditional approach, data transmission to earth would take weeks, hence those analyses are being performed onboard the ISS within minutes.
- Smart cities: Governments are beginning to experiment with EC as well, incorporating emerging technologies such as the IoT and AI/ML to quickly identify and remediate problems impacting public safety, citizen satisfaction, and environmental sustainability.
- In March 2021, Autonomy Institute, a US-based cooperative research consortium focused on advancing AI at the edge, announced plans to launch a Public Infrastructure Network Node (PINN) pilot at the Texas Military Department in Austin, Texas.
- PINN is set to be the first unified open standard incorporating EC, 5G, enhanced GPS, wireless, radar, lidar, and intelligent transportation systems (ITS) as a single unified system, according to an Intelligent Infrastructure article.
Outlook
In totality, EC will act more like a complementary technology to CC. Currently, the dependence on the cloud is so large that it will still be relevant in the long run. According to research by Gartner, EC is still at its nascent stage but will be supporting CC in nearly every enterprise by 2025.
This article was written by Sanjoy Gupta, SVP Business Development at Softtek. Visit his LinkedIn to contact him and learn more.


.webp?width=352&name=DALL%C2%B7E%202025-03-03%2011.27.07%20-%20A%20minimalist%2c%20abstract%20digital%20painting%20of%20a%20padlock%20shattering%20into%20geometric%20shards%2c%20symbolizing%20the%20breaking%20of%20encryption.%20The%20composition%20is%20slee%20(1).webp)
