Cloud Gaming: Moving the Action to the Edge

Cloud gaming adoption continues to grow as players and publishers now support game play anywhere and anytime. Read about the cloud gaming ecosystem and why it will continue its meteoric growth.
The Advent of Cloud Gaming
Video game popularity has grown significantly since the original MIT Spacewar! game was introduced in 1962. More recently, video games have provided an essential service to millions of isolated people during the Covid-19 pandemic. As the world slowly emerges from the pandemic, many gamers will face making new choices on how they pass the time every day.
The good news is that players will be able to take their games with them and play them anywhere and anytime. This capability has grown in recent years with the advent of cloud gaming.
What is Cloud Gaming?
Cloud gaming involves accessing a network connection to play games on devices (mobile or PC) from a game client located in an edge game server with close to game console video quality and performance.
But cloud gaming is more than streaming content to devices with content delivery network (CDN) technologies (e.g., Netflix, Disney+, YouTube). Many cloud gaming services process game data at multiple levels and stream customized low-latency data to players during gaming sessions. Cloud gaming architectures are generally organized into 3 primary levels, each of which performs distinct functions:
- Compute Endpoint is the mobile device or PC the player uses to access the game portal and play games. Gamers may also use a thin client (a device that runs from resources stored on a central server instead of a localized hard drive) to access the game. At least 10-15 Mbps of bandwidth is recommended (for comparison, 5Mbps is recommended for Netflix HD and 3Mbps for Zoom video conferencing).
- Frontend – Dedicated Game Server and Game Platform Services (hyper-local near the player): Game servers host the game, and game platform services provide features including leaderboards, matchmaking, chat, inventory management, and game service analytics.
- Backend – Game Database and Analytics Services (regional or central) manage the game system of record (game state), store and query analytics and gameplay events, and keep the dedicated game servers updated with the most recent versions of the game.
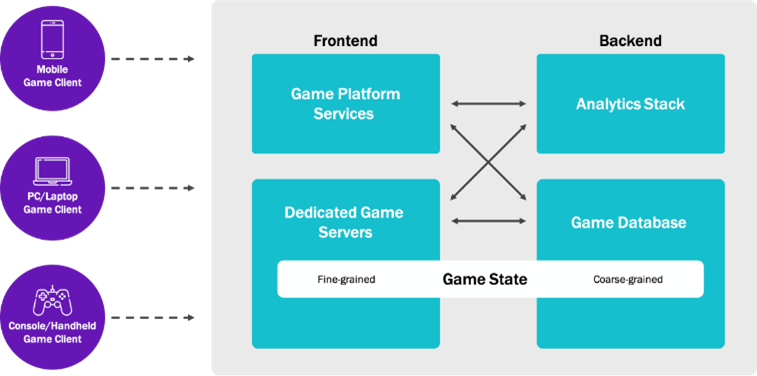
Figure 1: Example of a Cloud Gaming Architecture (inspired by Google Cloud Platform)
Cloud gaming frontend and backend infrastructure can be organized into public and hybrid cloud configurations.
The objective of cloud gaming services is to enable local gameplay performance levels remotely by minimizing data communications (data frequency and gravity) and increasing computing near the network edge.
International Cloud Gaming Market
The cloud gaming market has grown rapidly during the past few years, from $170M in 2019 to $585M in 2020 (244% increase), with projected growth to over $4.8B in 2023. North America (39%) and Europe (29%) account for more than two-thirds of the current sales volume.
At least 15 companies are currently providing cloud gaming services, from major game publishers (e.g., Sony PlayStation Now, Xbox Cloud Gaming) and internet giants (e.g., Amazon Luna, Google Stadia, CLOUD.GOOGLE, Facebook PlayGiga) to startups (e.g., Parsec, Shadow, PlayHatch, Paperspace).
The recent growth of cloud gaming is due to several drivers:
- Video game publishers have increased AAA (major game releases) and other popular games available to their own and other cloud gaming services. Examples include Assassin’s Creed, Doom Eternal, Fallout 4, and Overwatch
- Widespread adoption of “Games as a Service” business models with a library of games offered for a monthly subscription and third-party game publisher access
- Developers increasingly focused on enabling cross-platform play
- The continued evolution of subscription and free-to-play (F2P) game designs that spread the revenue over the life of the games.
- The growing availability of 5G and other high-bandwidth wireless connections
- Ongoing advancements in endpoint devices, including advanced video graphics, faster processors, increased storage, and decreased size at a reduced cost.
- Able to optimize cloud performance by performing heavy computations (e.g., graphics rendering, big data analytics) in the cloud and light computations (e.g., visual display) at the device level.
- Advanced security features which improve player data protection and reduce DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.
- Efforts to build on video streaming networks’ success (e.g., user interface design, player-named personas, game art visuals, search capabilities)
- Cloud gaming’s unique value proposition to both players and service providers (below).
Why Cloud Gaming?
For the player, cloud gaming provides several advantages, including:
- Gameplay is portable and can be played wherever there is an internet-connected desktop, laptop, tablet, or mobile device.
- The player usually does not need to upgrade their device to play games from the cloud.
- The latest version of the game is hosted on the dedicated game server, eliminating download time and local device storage limitations. Storage is limited only to what is required to play the game on a real-time basis.
- Games are available to the player without requiring a full-price commitment—test or rent games without downloading them first.
- Games as a Service increases the variety of games available to players.
For the Cloud Gaming service provider, benefits include:
- Enabling new models to monetize and retain players with personalized gameplay experiences.
- The cloud-centricity of cloud gaming enables companies to accelerate their cloud adoption progress with improved efficiency, automated scaling, and reduced cost.
- Increased reach and leverage of game content across multiple platforms.
- Improved secure access service edge (SASE)-based security.
Future of Cloud Gaming
The sustained benefits of cloud gaming are driven by our continued move toward the ubiquity of computing, mobile device usage and performance, wide content distribution, on-demand entertainment, and analytics-driven personalized player experiences. As the video game industry continues the quest for effective business models, cloud gaming will continue to disrupt the industry as we know it.



.jpg?width=352&name=florian-olivo-Mf23RF8xArY-unsplash%20(1).jpg)