Banking IoT to $2.547 billion by 2024

The growing number of smartphone users over the past decade has boosted IoT in the banking and financial services market. Several banks and other financial institutions offer mobile banking and online payments services, among other services.
In 2016, the number of smartphone users worldwide reached 2.1 billion, compared to 1.86 billion in 2015 and this number has been increasing progressively. Given this increase, financial institutions are expected to adopt IoT technology to optimize their payment services and processes.
Many banking entities have announced in recent years their plan to offer mortgage plans to their customers through their smartphones, as well as providing the ease of scanning and verifying the documents required by customers in the mobile banking app.
Greater investment will offer greater profit
The convergence of operational technology, information and increasing use of IoT devices in the monitoring of products, applications and premises that encompass connected banking, will make institutions consider investing greater percentage to improve.
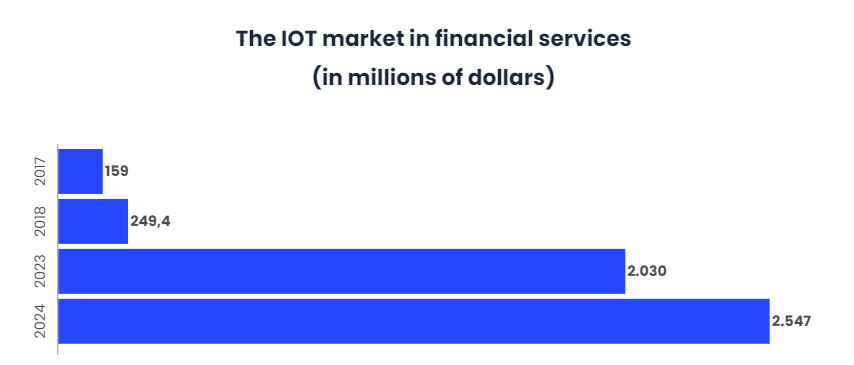
The size of the IoT market in banking and financial services is expected to grow from $249.4 million in 2018 to $2.547 billion by 2024.
Despite the doubts surrounding large-scale implementation, most CEOs in this industry already understand the value of this technology. Most (52%) believe that IoT’s ultimate goals focus on improving core financial sector processes.
These investments, and therefore market value, will be gathered in applications for data management, cybersecurity, proactive services, product planning and marketing, customer relationship management and analysis of data. In addition to components (hardware, software and services) and finally in applications aimed at the customer (insurance companies, mortgage companies, brokerage companies and others) in addition to private customers.
In particular, the insurance segment is expected to have the largest share of banking and financial services in the banking and financial services market in terms of the Internet of Things.
For example, with the emergence of autonomous vehicles, driver behaviour data can now be transmitted to auto insurance companies, so that they can assess drivers’ risks and premiums accordingly. This technology enables auto finance companies to reduce loan risks by at least 30%.
In general, in the union between IoT and the financial world the main areas that will hoard investment are:
- Tailor-made marketing:
These days, customers in all industries have started demanding customized solutions for their different needs, and this also applies to the banking industry. However, a bank can only tailor solutions for a customer if it has the necessary information about their purchasing behavior, current economic situation, and individual needs.
With IoT devices, banks may track all of their individual customers’ activities and then propose a specific solution for their desires and needs.
- Wearables:
Portable technologies are rapidly gaining popularity, and due to their widespread adoption, banks around the world are determined to enable banking through these wearables.
Currently, smartwatches have to be connected to mobile phones, but separate portable devices are also being developed, making them an interesting point for banking innovation.
The apps have already been developed and are offering basic banking activities, and are expected to introduce a horde of additional features and functions in the coming years to make banking services more accessible.
- Product planning and management:
IoT will prove invaluable in the banking industry to improve its products. For example, this technology can help banks provide their debit and credit card holders with a more rewarding experience.
Through the collection and evaluation of ATM data in different locations, you can highlight the areas that receive the most pedestrian traffic to take decisions regarding ATM facility locations.
- Better a of the security:
Security is of paramount importance in the banking system. A bank can only operate with the trust of its clientele and, with the many options available, people only work with banks that can offer them the greatest security.
IoT will greatly help banks in this regard in the future, as it can help introduce a robust identity verification and privacy protection system.
Biometrics are already being widely used, and the geolocation capabilities of mobile devices have also been useful in the verification and security process. IoT can help banks take this further and improve security for the peace of mind of their customers.
Concerns revolve around security and privacy
With regard to the last point, the introduction of new devices that may jeopardize the economic integrity of customers may lead to an initial rejection in them.
Globally, the number of connected devices is expected to exceed 20 billion by 2023, so it is important that companies, and in particular banking institutions, act quickly to ensure that the detection of a violation IoT system is as effective as possible.
Currently, a percentage of 13% of budgets are already earmarked for the protection and cybersecurity of connected devices. In addition, the 90% institutions believe that this expense is a very good consideration towards customers.
However, these efforts are not always effective at 100%, so organizations call on governments to intervene, a 79% calls for stronger rules on IoT security, and a 59% seeks clarification on who is responsible for protecting the IoT system.
While many governments have already approved or announced the introduction of ioT security regulations, most financial institutions (95%) believe that more uniform regulations should exist.
One example is the Japanese government, which passed an amendment to the law that allows its workers to hack people’s IoT devices as part of an extraordinary overhaul of insecure IoT devices.
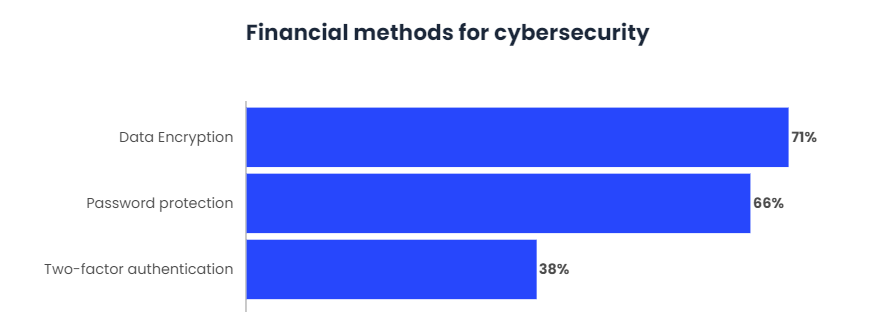
Meanwhile, companies continue to use other methods to protect themselves against cybercriminals. Most (71%) encrypt your data, while password protection (66) and two-factor authentication (38%) remain prominent.
However, the adoption of blockchain technology has increased to 19% in the last 12 months. A 23% institutions believe that blockchain technology would be an ideal solution to protect IoT devices; and 91% of the organizations that do not currently use the technology will likely consider it in the future.
With regard to banks’ customers, 71% states that, if their bank were to compromise their data through IoT technology, it would abandon the financial institution for one that would give it greater security.
Business alignment and affordability
Security and interoperability issues remain a sensitive point for IoT as already explained. However, device manufacturers are rapidly advancing on improvements.
Financial services companies have a lot to gain by integrating IoT devices into existing systems and workflows. Strategic implementations and successful management create a variety of business benefits:
- Reduced risk management :
The biggest benefit of IoT for financial services is real-time data feedback. By gaining information about internal and customer assets, many of these companies can integrate other innovations such as artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
This means an improved business understanding of customer behavior, global industry, and product/service change effect.
In addition to deeper customer knowledge and more agile mobile technology, IoT devices can also be used to save businesses money. The use of these devices reduces the expense of a building management system by up to 30%.
Considering that one of these systems can cost an office to install hundreds of thousands of dollars, IoT creates a tremendous opportunity to reduce costandsand amortize the investment.
- Best commitments:
Real-time data gives this financial industry the ability to anticipate future customer needs and concerns. And, therefore, by responding immediately to these forward-looking requests, customer experiences are updated, loyalty is improved, and over time, the number of new business opportunities increases.
The Internet of Things provides a technical framework that is able to create personalized offers and rewards for customers. If a user population is very committed to a specific product or service, or if sensors detect that someone has become stuck for an extended period online in a physical branch, new offers can be made more accessible and existing services can be tailored to the individual. To add even more value and relevance.
Europe will experience higher growth
The Asia-Pacific area will maintain its leadership in IoT adoption for financial services, due to the dynamic adoption of new technologies and aggressive initiatives to boost the IoT ecosystem, enabling commercial users will adopt cutting-edge technologies. Singapore, Japan and India are the main countries working to adopt IoT technology.
An example of this is the initiative carried out by the Singapore Infocomm Development Authority (IDA) and the Information Technology Standards Committee (ITSC), called SPRING Singapore, which encourages industry participants to make new developments and investments in the IoT sector.
55% of the organizations in this area, including financial institutions, have adopted an agile business model enabled by IoT.
However, despite the leadership of the APAC area, Europe will experience the greatest growth in the adoption of IoT technology for banking and financial services until 2024, due to the increase in investments made in technology by several European nations.
The United Kingdom, Germany, France and Russia will contribute significantly to this market over the next five years, the importance of these countries due to the strong presence of a tech-savvy population, which is expected to tilt the demand for connected devices.
In the case of Spain, this growth can be reduced due to the high number of cyberattacks received on IoT devices.
Finally, the Middle East and Africa are also expected to have a significant market share by 2024, due to the increasing adoption of IoT in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, among other economically advanced nations in the Region.
Conclusions
Some of the economic and technical factors that have caused the massive application of IoT will not be the best for the financial industry. However, some of them can have a fundamental impact on the functioning of the banking market.
IoT as a technology is an interesting tool for the financial industry, providing opportunities to constantly increase automation and improve data utilization techniques.
Over time, technology is expected to progress at an even faster pace, and financial institutions that understand its value will work to embrace it in its usual operation.
However, in order to use the full potential of IoT in the future, it is important to realize that improvements are needed in terms of connecting different devices with a higher degree of accuracy.
For IoT to work efficiently, it is necessary to establish harmony between different components, such as sensors, edge devices, mobile technology, etc.


