The insurance industry prepares for a Post-Covid scenario

The year 2020 started with the same dynamics as 2019 for the insurance sector. January saw a certain increase in the percentage of projects and emissions per insurer. However, in February, at the same time that the health alert grew due to the increase in cases of coronavirus, the activity in the distribution of insurance decreased by 4% in emissions and 7% in projects.
March showed a significant reduction in activity since the 11th, when the WHO declared the coronavirus a global pandemic. Since then, the national insurance sector has invested around 50 million euros in collaborative projects to tackle the virus.
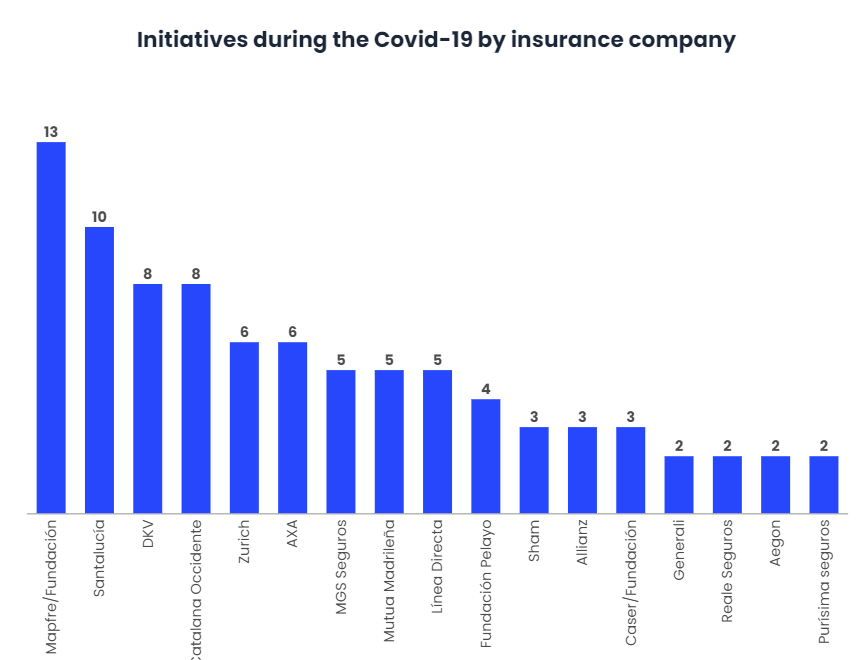
The funds have been used to help vulnerable groups, to purchase health equipment, to finance medical research projects and to provide support for health workers. All with the aim of facing the crisis in the best possible way and thinking about the prompt reactivation of the activity.
In addition to the insurers’ duty to collaborate at the social level, there is also the concern to protect the health and safety of employees and partners, while at the management level, the entrepreneurs try to maintain the continuity of their business.
This leads to other headaches for insurers, such as the economic stability of the company and its workforce, redirection to new emergency and response operating models, and a new set of safety protocols that can be adapted to the difficulties that may arise as the crisis continues to unfold.
Impact of Covid-19 on the insurance sector
The state of alarm has led to a decrease in the marketing of insurance, negatively affecting the insurance sector. According to the data, senior insurance executives agree that the drop in sales has been the aspect of the business that has suffered the most, followed by the financial situation (30%) and the increase in the accident rate (13%).
The main consequences of the Covid-19 in the insurance sector show differences according to the branches of business:
- The development of home and auto insurance has remained similar to that of GDP, which has shown a downward trend in recent years.
- Health insurance may behave in a counter-cyclical way, different from previous periods, as it is directly related to the crisis itself.
- In savings life, the negative trend of recent years will be accentuated.
- During the crisis, the arrival of new individual clients has decreased by almost 60%, while at the level of companies, the decrease in contracting has been up to 80%.
- Cancellation percentages will increase to 15% in relation to current ones, varying according to the type of risk.
- The accident rate has been lower than usual due to the lower incidence of car and travel insurance.
- The accident rate has increased in terms of non-payment of rent, life and death.
Depending on the size of the insurance company, it is clear that small brokerages have been most affected, with differences of up to 7% in projects and 8% in emissions. On a national level, the autonomous communities most affected have been Murcia, Valencia and Extremadura, which suffered reductions of over 60%. Among the communities that experienced a fall of less than 40% are Aragon, Asturias and Madrid.
According to data in this first quarter, the impact of Covid-19 on the insurance industry is probably deeper and broader than it currently appears, and could last until the third quarter or longer. As a result of the virus’ effects, global GDP growth in 2020 could drop by as much as 1%, from 3.3% to 2.3%, making recovery in 2021 unlikely.
According to estimates, a longer and more intensive outbreak could reduce global growth to only 1.5 per cent in 2020.
Insurance companies face the post-covid era
The new normality brings with it a new style of demand, and new opportunities for insurers to do business:
- Event and travel cancellation insurance will become widespread for public and private events, including weddings. On trips, coverage will be greater on trips abroad and will be combined with medical care and other more specific coverage in case of contagion by Covid-19.
- It is estimated that the purchase of health insurance will increase with the deployment of telemedicine and remote assistance systems. In this sense, insurance companies will relieve the workload of hospitals with solutions such as virtual assistance and video consultation.
- The more teleworking, the more cyber attacks. Hackers use various techniques to evade the security of companies, through phishing, spam, malware, have tried to steal credentials to access critical data of companies. Looking at the current teleworking landscape, it is expected that there will be an increase in the hiring of cyber security and cyber insurance tools to maintain the confidentiality of business and employee data. The average cost of claims affecting this type of company is estimated at 31,000 euros.
- A change in the way of taking out insurance is expected, young people will be increasingly interested in taking out insurance, especially life and travel insurance with specialized coverage in Covid-19 situations.
- More and more private individuals will take out insurance for non-payment of rent. It is clear that during the pandemic and due to the confinement and cessation of activity, many owners have not covered
- D&O: growth is expected in the civil liability area, and the introduction of pandemic risk exclusions in new contracts and policy renewals will begin.
The digital transformation as an answer
The evolution of the crisis forced companies to adopt new, more flexible and therefore more digital operating models. Many created their own model of the epidemic to anticipate the negative effects of the virus and design plans to respond more effectively in the long term.
The pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of the insurance industry. The digital enterprise seeks to improve connectivity, automation and operational optimization of its processes. Efficient, digital companies conduct their planning, budgeting and financial forecasting in a simple and collaborative manner, paying special attention to the user and offering a global vision of the company.
Some of the main trends that have come to the industry and have been strengthened as a result of Covid-19 are:
- Digitization. The appearance of new companies or 100% digital apps, and the adaptation of the most traditional branch of the insurance sector to the new technologies, to compete in agility and flexibility before the movements of the market. In addition, confinement and social distance have led companies to telework and seek new digital solutions, such as the use of tele-assessment tools, video consultation and telemedicine.
- Big data and advanced analytics. Companies have adopted this technology to identify, quantify and prioritize risks. The data and analysis of these will allow companies to customize policies for each user, offering a better service and anticipating unforeseen events. No two policies will be the same.
- The arrival of the Blockchain will mean a reduction in verification costs and data storage, while allowing companies to tackle fraud cases more quickly, making the accounting process much more transparent. The technology is expected to move more than $1.3 billion in the insurance market by 2023.
- Investment in cybersecurity systems will increase as a result of the rise in cyber attacks during the pandemic. New software will be adopted to safeguard data and regulatory compliance software.
- The cloud will allow insurance companies to improve accessibility to data, offering it in real time, and giving the opportunity to attend to incidents virtually through virtual switchboards with greater possibilities than other traditional methods, which translates into better customer service.
A good example of the industry’s intention to adopt technology to accelerate digitization is the recent collaboration between MSG Life and Signaturit. The idea of the companies is to facilitate and speed up the process of electronic signature of documents, preserving the legal validity of the same. This will help improve the process of welcoming their new customers, which will become 100% digital and will take place in a matter of minutes, without any travel or added inconvenience to the user experience. At the same time, the electronic signature will reduce costs, optimizing the time spent and facilitating the centralization of information.
Conclusions
The insurance sector is prepared for a possible second wave of the Covid-19, and also foresees mergers between traditional companies and Insurtechs to facilitate digitalization by increasing the budget, and thus improve effectiveness and response capacity to the crisis. It is possible that entities already suffering from solvency problems will opt to merge with each other to become more competitive. At staffing level, a reduction and freezing of recruitment is expected. While the vast majority of projects are continuing as usual.
On the other hand, the reputation of insurance companies has improved thanks to the various social actions they have carried out during the pandemic.
In addition, clients are reconsidering how to make an appointment with a broker to take out a policy. These are times of social alienation. For this reason, among others, many have switched to 100% digital insurance companies, which represents a danger for traditional insurance companies that do not have a digital renewal plan, and at the same time shows a great business opportunity.


