Smart Working: Much more than telework

At the beginning of this year, a large number of companies worldwide still believed that physical assistance to the worker at his or her workplace resulted in increased productivity. In fact, until the beginning of 2020 only 7% of Spanish workers ever teleworked.
The vast majority of companies did not opt for this working model, however, the arrival of COVID-19, confinement and social distancing has forced many companies to transform themselves digitally and adopt new working models to keep operations running.
Faced with this new situation, many companies decided to implement teleworking in order to send their workers to work from home. However, many others wanted to go further, and implemented the so-called Smart Working, a new working model that merges teleworking with new technologies, so that workers are completely autonomous and have all the resources they need to carry out their work in the way they consider best.
A new working model
Therefore, Smart Working can be defined as a new management philosophy based on giving workers flexibility and autonomy both in the choice of workspace, timetables, as well as the tools to be used, but with greater responsibility for results. It implies rethinking the ways in which work is done, eliminating the limitations derived from being in a fixed space and from traditional office models that are at odds with the principles of personalisation, flexibility and virtuality.
When a company implements teleworking it means that it has its workers working from a specific, stable location, which, although that location is not the office, and it is usually at home, they still have to comply with a series of rules, timetables and continue to use tools established by the company.
In the case of Smart Working, these limitations are overcome, as the worker has absolute freedom to decide at all times where to work from (home, airport, train, coworking, hotel, restaurants, bars, waiting rooms, etc.), even if it is from a different place every day and has absolute mobility; what their working hours will be, which can also be different every day; and what tools they want to use to do their job.
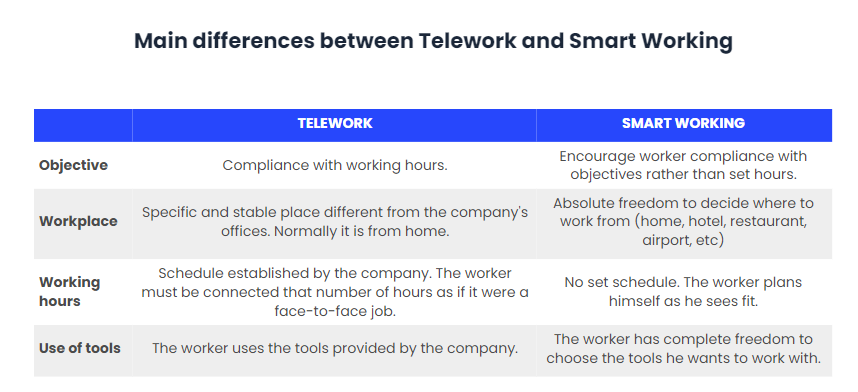
This working methodology is based on trust between the company and the worker, on clear and transparent communication between the two, and on the worker’s compliance with his or her objectives. The aim is not for the worker to work a series of established hours, but rather for him/her to fulfil the objectives that he/she has. In order to achieve this, good coordination is needed on both sides.
Main features of the Smart Working
Smart Working not only aims to achieve a balance between employees’ work and personal lives, but also to bring about a cultural change and an evolution of corporate organisational models. This requires a detailed, phased roadmap that is consistent with the technological, cultural and management nuances of the organisation.
This is why technology plays a key role. Smart Working requires a digital transformation in the workplace, the application of technologies to connect people, spaces, tools and business processes, to achieve efficiency and effectiveness that maximise productivity while meeting business objectives and priorities.
In any case, the Smart Working methodology has a series of important characteristics that determine what it means:
- Mobility and teleworking: As mentioned above, teleworking is a fundamental pillar of Smart Working, as employees working according to this methodology are teleworkers who can freely choose where they want to work, and can even work from a different location each day if they so wish.
- Achieving objectives: Smart Working is a working model that works entirely on the basis of concrete objectives. The company assigns the worker a series of objectives in accordance with their abilities and agrees on delivery times. The worker must organize to meet them.
- Optimised time and schedule management: Workers who work under this methodology must be very disciplined, since once the objectives or projects have been assigned it is the worker himself who manages them and sets the schedule that he considers best. This improves the worker’s work-life balance, as well as their performance.
- Trust: Trust between employees and the company is key to making Smart Working possible. Each employee is responsible for delivering work on time, or for communicating any problems that may arise, and the company must be confident that this will be the case.
- Technology: The key to this methodology lies in the use of technology, as without it, Smart Working would not be possible. Organisations must be up to date with the latest technological advances. From Internet connections to cloud tools, cyber security or communication tools (video calls), technology makes it possible to optimise processes and speed up projects. Workers must have all the tools and technological resources necessary to do their job in the best possible way.
- Communication as the main concern: For this methodology to work, workers must know how to communicate with the company and must feel that they are never alone, even though they are not physically in the office. Communications must be very fluid and transparent.
Benefits and disadvantages of the implementation of Smart Working
With all the above, there is no doubt that the Smart Working has many advantages, not only for workers, but also for companies. And it is precisely for this reason that more and more companies in different sectors are deciding to implement this methodology:
- Working by objectives makes the worker more motivated and committed.
- This is also helped by the fact that the worker can organise his working day as he sees fit, according to his needs. They can take breaks when they need to, for example, exercise.
- Furthermore, being able to work from any location improves the balance between family and personal life, and therefore increases satisfaction and work-life balance.
- Travel costs are reduced, as well as the time, resources and stress for workers caused by travelling to the office.
- This reduction in travel also has an impact on the environment as CO2 emissions are also reduced, and with the arrival of COVID-19 this methodology has helped prevent the spread of the virus, as well as helping to ensure that if there is an outbreak of flu, workers do not become ill.
- The company is freed from the need to continually monitor the work being done, meetings are shorter and more focused, and there are fewer unnecessary breaks.
- A company prepared for Smart Working is more resistant to external factors, i.e. being able to work from anywhere and at any time guarantees business continuity, which limits possible crises caused by forced interruptions.
- With Smart Working, teams can be multicultural and multidisciplinary.
- In relation to the previous point, this methodology encourages the attraction and retention of talent, as having the workers offshored means that they can be hired from anywhere in the world, focusing exclusively on their skills and abilities and not on whether or not they are close to the office. This has become a differentiating element among employees.
However, the Smart Working is not a perfect working model, and it also raises several concerns. Working outside the office can reduce worker commitment by increasing distractions. In addition, by reducing interactions between workers and between workers and their bosses, there is a risk of worker isolation and reduced productivity. Also, blurring the boundaries between work and home can increase overtime and stress levels for employees.
It is true that Smart Working is not a suitable solution for all companies, for example, companies that are facing the public cannot have freedom of time and location, but it is also true that many companies let fear of losing control over employees stop them from deciding not to implement this methodology, and this causes them to lose the many advantages it has.
The models that articulate the Smart Working
In the end, it is the companies that decide whether it will be beneficial to implement this working methodology, and if they want to do so they must decide how and in what way. To be able to make this decision better, it is important to know all the models that articulate Smart Working:
- Agile Working: The aim is to give more importance to projects and results, giving the worker the autonomy, freedom and flexibility they need. It is based on the trust and responsibility of workers who have the freedom to work where, when and how they want. Agile Working aims to create more responsive, efficient and effective organisations based on more balanced, motivated, innovative and productive teams and individuals.
- Activity Based Working: This is an evolution of what is known as ‘office work’, creating adaptive workspaces where flexibility and collaboration are encouraged. It is the team that decides the best way to work by designing their own space.
- Knowledge-Based Working: This methodology uses technology such as Artificial Intelligence, predictive models and data analysis to understand the behaviour and needs of both workers and clients. In this way, work can be adapted to those needs and behaviours.
- Experience-Based Working: Every day more workers prioritise the experiences that a job can bring them in order to decide between one job or another, or between one company and another. The connection with the company, with colleagues and with the work being done, the flexibility to work from wherever they want and whenever they want, generates a series of well-being experiences.
Conclusions
The arrival of COVID-19 has been a turning point in the transformation process of companies, and those that were able to react and implement methodologies such as Smart Working have obtained more efficient results, and the impact on business continuity has not been so negative.
Smart Working is a form of teleworking, but more effective and efficient, which focuses on results, and offers a series of benefits for both employees and companies that must be taken into account.
In spite of the circumstances that are being experienced today, it is an opportunity to think, to restart, and to reinvent oneself at a business and individual level. The Smart Work is the new reality, and if it is well implemented, companies will become more productive, competitive and aware. With this methodology, new commercial opportunities will also appear that will make the company prosper and survive extreme situations such as the COVID-19 crisis.
Companies must be aware of the changes they are facing. The new digital era implies many challenges and the ability to adapt companies and teams to a new working culture.


