New trends in Databases

During the year 2020, the different companies that exist have become more digitised, being practically impossible to avoid the use of databases and Big Data. Currently, it is necessary to have the ability to obtain information from data, this being a key aspect for any successful organisation. Therefore, any information architecture must continue to be based on databases.
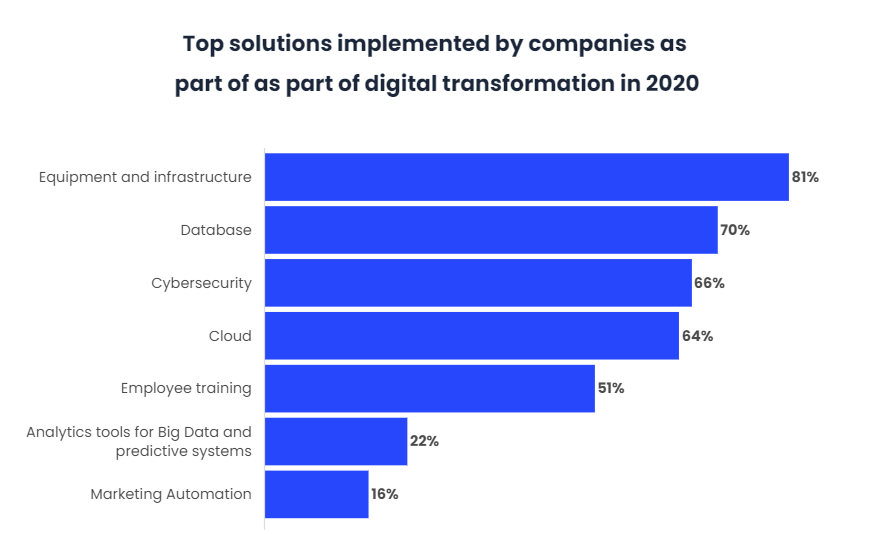
Among the main utilities that a database provides to a company is to group all the company’s data in the same place, to facilitate the sharing of data between the different departments of the company, to avoid redundancy and to improve the organisation together with an adequate interlocution with the company’s clients. Thus, if a database is properly managed, benefits such as increased efficiency, simplification of the process, greater security of the stored data and greater productivity can be obtained, among other advantages.
In this analysis we will describe different database trends that can help any company to improve the management of its data and information in order to thrive successfully.
HTAP: Big data plus database
In the field of applications, the concept of Big Data and databases come together. Thus, for applications with a single system, data generation, processing, storage and consumption can be performed, resulting in a better user experience.
At this point, hybrid transaction processing or analytics, also known as HTAP, emerges, which improves performance and is able to synchronise millions of transactions daily, improving the user experience.
Soon, this trend is expected to grow, as HTAP databases can also be used as data warehouses, handle online transactional processing (OLTP) workloads and respond quickly to real-time Big Data analytics requests.
A more distributed cloud-native system
The fact that more and more companies are adopting cloud-based infrastructure means that they are moving their business process applications along with their critical applications and data.
By 2022, it is estimated that 75% of all databases will migrate to a cloud platform. Therefore, organisations require cloud services and solutions that manage their native architecture, enabling business processes to be more dynamic.
A cloud-native system therefore means that applications or processes run in software containers as isolated units, processes are managed through central orchestration to improve resource usage and reduce maintenance costs, and applications are loosely coupled. These characteristics refer to a highly dynamic system composed of independent processes working together to deliver business value, i.e. a distributed system.
Thus, combining distributed processing techniques, without a heavy infrastructure setup, will allow users to enjoy high availability thanks to efficient cloud-native databases.
Intelligent and autonomous database platforms
On the other hand, Self-Driving Database Platforms (SDDPs) provide self-driving capabilities to databases running on a platform, allowing databases to independently sense, make decisions and perform optimisations in order to generate continuous service.
In addition, SDDP brings with it other capabilities such as physical resource management, instance lifetime management, security and automatic scaling.
It is expected that in the future, databases will be fully autonomous, allowing routing to be fully automated in a database. However, full automation is complex when companies often change databases, making it difficult to automate the entire process.
Today, AI can be used for different scenarios in the database domain, such as workloads or application in legacy systems to adjust parameters and improve scalability, all using machine learning algorithms to ensure that they are secure and run smoothly.
Multimodel
Multi-model databases are also available, which are characterised as data processing platforms that support multiple data models and define the parameters of how information is organised in a database. The advantage of incorporating multiple models into a single database is the ability for IT teams to meet various application requirements without the need to implement different systems in the databases.
Also, the data models that can be accommodated by these databases include relational, hierarchical and object models, as well as different styles of documents or graphs, including those that are part of NoSQL databases. Another characteristic of this type of database is that they do not store data uniformly in a row-based table structure, so they can handle different forms of data that do not conform to the rigid schema of the relational model, including unstructured and semi-structured data.
However, in some situations this multi-model approach can impede the transactional integrity that relational database management systems use to maintain data consistency.
Built-in security
In any application, interface, product and business, security is a necessary and fundamental requirement. In the current digitalisation process, it is essential to maintain high levels of trust and transparency, where data is secured.
Therefore, techniques such as encryption in motion with transparent data encryption (TDE), flexible key management, encryption at rest, traceability and auditing are necessary and mandatory for any company.
Among those mentioned, the TDE technique, used to encrypt SQL Server and Azure SQL Database data files, stands out. In addition, it allows encrypting confidential data in databases and protecting the keys used to encrypt data with a certificate.
This type of security technique helps with industry and cybersecurity regulations and guidelines, so that if a cybercriminal tries to steal data files, they would not be able to use them because they would need a key to access them. However, it is important to know that TDE only adds a layer of protection for data at rest and the remaining risks must be protected in the file system of the operating system and the hardware layer.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the world is digitising at a rapid pace, so the search for different techniques to deal with heterogeneous data is a challenge for companies looking to make the most of the latest technology advances such as AI or IoT.
Studies of new alternatives for cloud databases seek to make storage and computation compatible with a wide variety of open source interfaces.
For example, new database types will support different table models with wider columns or time series, storage and analysis of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. This will result in increased performance of smart devices requiring multi-model data storage, metadata analysis, time series data and device logs.
In the future, we will look to combine bolckchain technology to provide immutable modifications to database systems, and seek to leverage new hardware to encrypt data and process it without the need to decrypt it in databases.


