COVID-19 and its impact on Cybersecurity

The COVID-19 pandemic has brought an immense humanitarian crisis that has also severely affected the world economy. The rapid and unexpected interruption of all activity for companies around the world has left them struggling to maintain security and continuity of their business.
As organizations have had to move to work from home to protect their workers while continuing to serve their customers, they have moved most of their business into the digital world, greatly increasing the risk of cyber attacks. Their main challenge has become how to secure new teleworking practices while ensuring that core business functions operate without interruption, as well as how to keep the organization safe from cybercriminals who take advantage of the uncertainty of the situation.
Cybercriminals are using the unfamiliarity that exists with teleworking to take advantage of companies that do not have good protocols for working from home.
Present situation
Since the arrival of the pandemic and the lockdown, an increase in phishing attacks, malware, data breaches and ransomware attacks has been observed, as attackers use the COVID-19 as bait to impersonate brands that mislead their employees and customers. This has resulted in an increase in infected PCs and smartphones.
These attacks not only affect businesses, but also end users who, for example, download COVID-19-related applications, convinced that they are legitimate applications, and instead download ransomware. In fact, during this time, more than 30,100 domains were registered in connection with the pandemic, of which 131 were identified as malicious and 2,777 as suspicious.
With the implementation of teleworking and communications between people reduced to calls and video calls, security breaches have increased, in fact, according to the latest data, during the first quarter of 2020, cyber attacks increased by 125% in Europe and 40% globally.
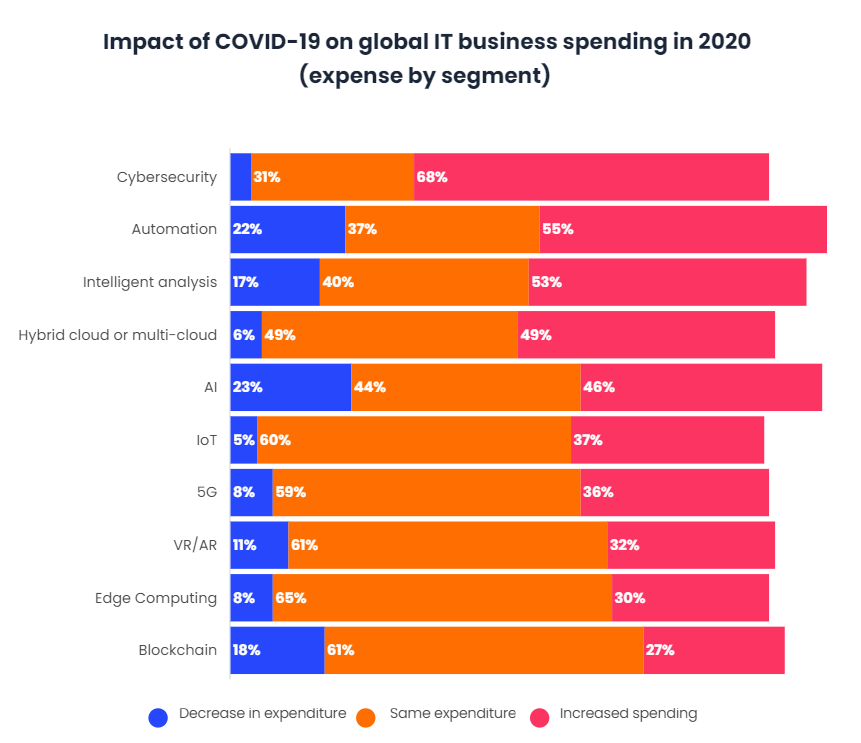
However, this rise in cybercrime has caused both organizations and users to become much more cautious, with 68% of major companies, both public and private, planning to increase their spending on cybersecurity.
According to the data, cybersecurity spending has increased recently. In 2017, companies worldwide spent $34 billion on cybersecurity solutions. Before the coronavirus outbreak, it was estimated that this amount could reach $42 billion by the end of 2020. However, with the COVID-19 crisis creating new opportunities for cybercriminals, this figure is likely to increase by the end of the year.
What have been the main threats?
Cybercriminals look for recklessness on the part of individuals in order to get into systems, and when a crisis situation, like this one, is prolonged in time, users tend to make more mistakes than usual, due to the stress and uncertainty of the situation. This increase in cyber attacks is reflected in real situations that have been occurring. For example, in these days of crisis, hospitals have been, for many cybercriminals, the focus of their attacks. In Spain, the National Police discovered ransomware, called NetWalker, which could block computers in hospitals and break the entire computer system. This virus was attached to e-mails sent to health professionals containing information about COVID-19, but when opened it contained this virus.
Some of today’s ransomware scams include:
- Information on vaccines, masks and products that have been in short supply, such as hand sanitizers.
- Financial scams offering to pay government institutions to help businesses because of the economic downturn.
- Free downloads of technological platforms that have been in great demand, in order to carry out teleworking and meetings from home, such as video call platforms.
- Necessary updates for business collaboration tools and social networking applications.
The creation of new ransomware techniques has been one of the main threats these months, however, it has not been the only one, by far. Phishing has also become widespread with the almost massive sending of emails impersonating banks and other institutions to steal data. Google reported that Gmail users receive 18 million phishing emails focused on the COVID-19 theme every day.
WhatsApp has also become a good tool for cybercriminals to send out various campaigns using the pandemic as an excuse. Some of the most common campaigns are the tips to stop the virus. The World Health Organization (WHO) was also supplanted by a phishing campaign asking for a donation, at Bitcoins, to help research against the pandemic.
Is there a ‘cyber-pandemic’ coming?
The new reality created by COVID-19 has brought an increase in threats in the field of cybersecurity. During this pandemic, technological evolution has been driven by moving almost all services to the digital world, but this change, which had to be made overnight, by force and from ignorance, has led to cybercriminals finding many gaps in security through which to access systems.
This pandemic has shown that the Internet is a critical and global part of any infrastructure. Home offices, as well as education and life, are increasingly dependent on each person’s ability to use the Internet. Therefore, protecting cyberspace is an increasingly necessary task.
The attacks that have been taking place during the pandemic have shown that they are capable of paralyzing all activity, for example, of a hospital, stealing hundreds of records and thousands of data, and stealing important information and then collecting a reward.
So is a cyber-pandemic looming? Some experts say it is and that we must be prepared for it. But whether it happens or not, what is clear is that companies, large or small, must optimize and improve their security protocols to ensure that they have a robust and comprehensive cybersecurity system.
Conclusions
The COVID-19 crisis has created unprecedented challenges for organizations. The rapid and unprecedented shift to telework has raised issues around digital security, mainly because cybercriminals have taken advantage of the current uncertainty and gaps in cyber protocols to get into the systems.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, industry leaders will need to address them to mitigate any potential harm to individuals and avoid disruption of key services, as this could have serious consequences for the economy.
Companies that understand the danger and take action, by implementing effective cyber risk management practices and cyber resilience, can adapt and make their businesses smarter, faster and more connected, by driving business growth and efficiency.


